Comprehensive Guide to Water Treatment Membranes: UF, NF, and RO Technologies
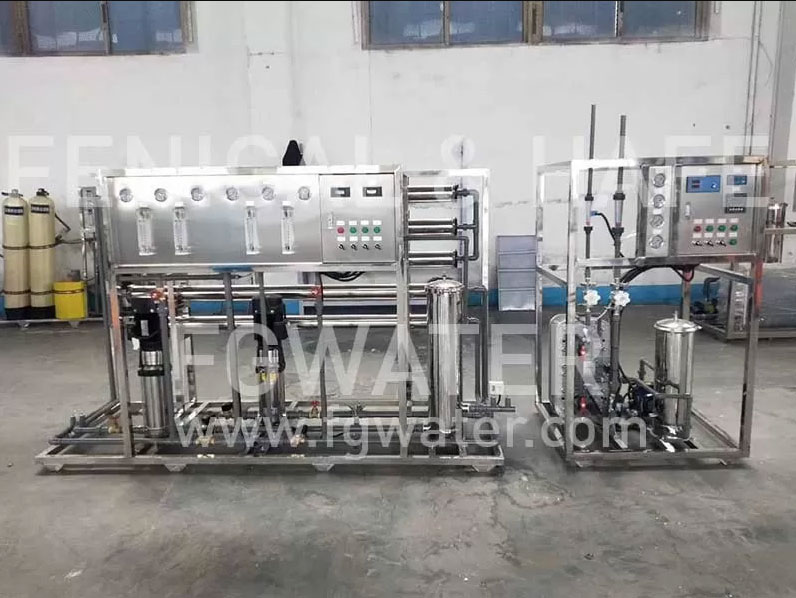

Ultrafiltration (UF), Nanofiltration (NF), and Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes Comparison
Water treatment membranes, such as ultrafiltration (UF), nanofiltration (NF), and reverse osmosis (RO), play crucial roles in various applications, from drinking water purification to wastewater treatment. Understanding the differences and suitable applications of these membranes helps to choose the right technology for your specific needs.

Nanofiltration (NF) Membranes
Pore Size: 0.001 microns (nanometer scale)
Key Applications: Removal of organic materials, colorants, hardness, and certain dissolved salts in surface water and groundwater, as well as extracting and concentrating useful substances in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Operating Pressure: 3.5-30 bar
Salt Rejection: 20%-98% (removes divalent ions better than monovalent ions)
Advantages: Cost-effective alternative to RO for medium-level purification.
Buy Nanofiltration Membranes Here
Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes
Pore Size: The finest of all, effectively removing dissolved salts and organic compounds with molecular weights above 100.
Key Applications: Widely used in desalination of seawater and brackish water, producing high-purity industrial water, and removing harmful chemicals like heavy metals, pesticides, and chlorinated compounds.
Operating Pressure: Varies with application
Advantages: Extremely high purification capabilities (up to 99% salt removal), suitable for high-quality water production in a range of industries.
Buy RO Systems Here: Seawater | Brackish Water
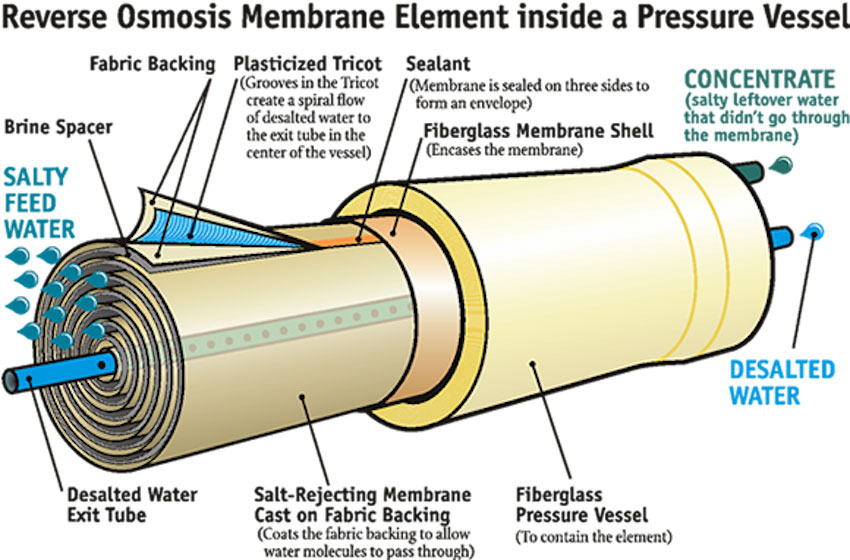
Ultrafiltration (UF) Membranes
Pore Size: 1-20 nanometers
Key Applications: Effective in removing larger particles, proteins, colloids, microorganisms, and large organic molecules, while allowing small molecules and dissolved solids to pass through.
Operating Pressure: 1-5 bar
Advantages: Simple design, low operating pressure, no chemicals needed, and high reliability. Ideal for purifying water with low to moderate contamination.
Buy UF Membranes Here
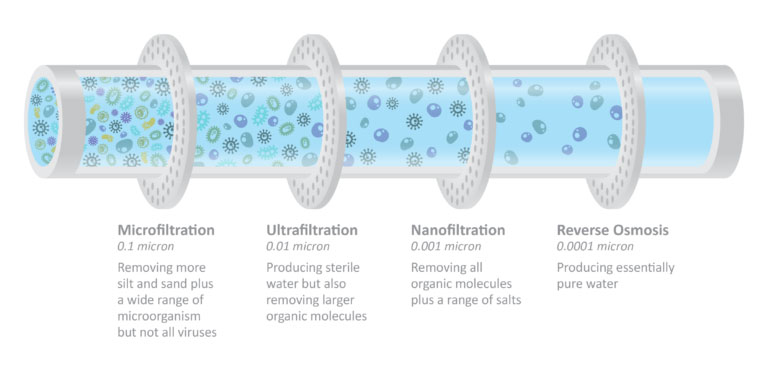
Comparing UF, NF, and RO: Key Differences
Filtration Precision: RO membranes have the smallest pore size, capable of removing nearly all contaminants, including salts and organic molecules. UF is typically used for larger particles and bacteria, while NF falls between UF and RO in terms of purification level.
Application Efficiency: UF systems are more energy-efficient and simpler to operate, making them ideal for low-cost and moderate purification needs. In contrast, RO systems are better suited for applications requiring high water purity, such as pharmaceutical or food production.
Water Quality: RO provides the highest water quality, making it suitable for sensitive industrial and drinking water applications. UF is effective for general filtration, and NF provides a balance of filtration and cost-efficiency for many municipal and industrial uses.

Advantages of Each Membrane Technology
Ultrafiltration (UF): Low energy consumption, no chemical requirements, simple setup, and relatively inexpensive. Ideal for biological molecule separation and water pre-treatment.
Nanofiltration (NF): Cost-effective solution for water softening, removing organic materials, and producing potable water from surface water sources. It also strikes a good balance between performance and cost.
Reverse Osmosis (RO): The most effective water purification method, particularly for desalination and removing dissolved contaminants like heavy metals, salts, and organic chemicals.
Applications in Water Treatment
Nanofiltration (NF): Drinking water purification, wastewater treatment for textiles, leather, and electroplating industries, and brackish water desalination.
Reverse Osmosis (RO): Desalination, industrial water production, wastewater reuse, and high-purity water production for pharmaceuticals, food, and electronics industries.
Ultrafiltration (UF): Pre-treatment for RO systems, drinking water filtration, food and beverage processing, and wastewater treatment.

Conclusion: Choosing the Right Membrane
Selecting the right membrane technology depends on the water quality, desired output, and cost considerations. UF is excellent for basic filtration and pre-treatment, NF serves as a good middle-ground for water softening and organic removal, while RO is the go-to for high-purity needs and complex water treatment systems.
For more information or to purchase any of our water treatment solutions, contact us here: Contact FG Water Technologies.